SECTION A: Multiple Choice Questions
1. The number of solutions of the equation  is:
is:
(A) None
(B) One
(C) Two
(D) More than two
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
2. The mean and the standard deviation (s.d.) of 10 observations are 20 and 2 respectively. Each of these 10 observations is multiplied by  and then reduced by
and then reduced by  , where
, where  and
and  . If the new mean and new s.d. become half of their original values, then
. If the new mean and new s.d. become half of their original values, then  is equal to:
is equal to:
(A) -20
(B) 10
(C) -10
(D) -5
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
3. Let  be the
be the  term of an A.P. If
term of an A.P. If  and
and  , then the common difference of A.P. is:
, then the common difference of A.P. is:
(A) 3
(B) 5
(C) 4
(D) 7
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
4. If the equation  has roots
has roots  , then the value of
, then the value of  is:
is:
(A) 104
(B) 8
(C) 13
(D) -104
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
5. Let 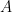 be a non-singular square matrix of order 3 such that
be a non-singular square matrix of order 3 such that  and
and  . If
. If  then:
then:
[Note: and
and  denote trace of square matrix
denote trace of square matrix 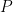 and adjoint matrix of square matrix
and adjoint matrix of square matrix 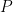 respectively.]
respectively.]
[Note:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
6. Match the column
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| (a) |
(p) 102 |
|
(b) In the figure, number of progressive ways to reach from (0, 0) to (4, 4) passing through point (2, 2) are:
[Insert Grid Image Here]
|
(q) 2300 |
| (c) The number of 4 digit numbers that can be made with the digits 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 2 | (r) 82 |
| (d) If |
(s) 36 |
(A) (a) → q; (b) → s; (c) → p; (d) → r
(B) (a) → p; (b) → s; (c) → r; (d) → q
(C) (a) → q; (b) → s; (c) → r; (d) → p
(D) (a) → p; (b) → s; (c) → p; (d) → r
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
7. Let 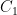 and
and  be two biased coins such that the probabilities of getting head in a single toss are
be two biased coins such that the probabilities of getting head in a single toss are  and
and  , respectively. Suppose
, respectively. Suppose 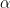 is the number of heads that appear when
is the number of heads that appear when 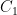 is tossed twice, independently, and suppose
is tossed twice, independently, and suppose 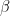 is the number of heads that appear when
is the number of heads that appear when  is tossed twice, independently. Then probability that the roots of the quadratic equation
is tossed twice, independently. Then probability that the roots of the quadratic equation  are real and equal is:
are real and equal is:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
8. If  are complex numbers such that
are complex numbers such that  ,
,  and
and  , then
, then  is equal to:
is equal to:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
9. If  , then
, then  is:
is:
(A) 20
(B) 32
(C) 22
(D) None
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
10. There are 3 bags A, B & C. Bag A contains 1 Red & 2 Green balls, bag B contains 2 Red & 1 Green balls and bag C contains only one green ball. One ball is drawn from bag A & put into bag B then one ball is drawn from B & put into bag C & finally one ball is drawn from bag C & put into bag A. When this operation is completed, probability that bag A contains 2 Red & 1 Green balls, is:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
11. If  is continuous at
is continuous at  , then value of
, then value of  and
and 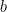 are:
are:
(A) 
(B) 2, 4
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
12.  is a function such that
is a function such that  and
and  . Also
. Also 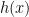 is a function such that
is a function such that ![h(x) = [f(x)]^2 + [g(x)]^2](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=h%28x%29+%3D+%5Bf%28x%29%5D%5E2+%2B+%5Bg%28x%29%5D%5E2&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) and
and  , then the value of
, then the value of  will be:
will be:
(A) 0
(B) 5
(C) 10
(D) 15
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
13. Let  be a function such that
be a function such that  ,
,  and
and  , then which of the following is correct?
, then which of the following is correct?
(A) 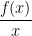 is differentiable in
is differentiable in 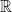
(B)  is continuous but not differentiable in
is continuous but not differentiable in 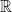
(C)  is continuous in
is continuous in 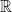
(D) None
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
14. If  for all
for all  and
and  and
and  , then the value of
, then the value of  must be:
must be:
(A) 2000
(B) 2500
(C) 3000
(D) 3500
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
15. Area enclosed between the curves  and
and  is:
is:
(A)  sq. units
sq. units
(B)  sq. units
sq. units
(C)  sq. units
sq. units
(D) None of these
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
16. The solution of  is:
is:
(A) ![\log \left[ 1 + \tan \left( \dfrac{x + y}{2} \right) \right] + c = 0](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Clog+%5Cleft%5B+1+%2B+%5Ctan+%5Cleft%28+%5Cdfrac%7Bx+%2B+y%7D%7B2%7D+%5Cright%29+%5Cright%5D+%2B+c+%3D+0&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002)
(B) ![\log \left[ 1 + \tan \left( \dfrac{x + y}{2} \right) \right] = x + c](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Clog+%5Cleft%5B+1+%2B+%5Ctan+%5Cleft%28+%5Cdfrac%7Bx+%2B+y%7D%7B2%7D+%5Cright%29+%5Cright%5D+%3D+x+%2B+c&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002)
(C) ![\log \left[ 1 - \tan \left( \dfrac{x + y}{2} \right) \right] = x + c](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Clog+%5Cleft%5B+1+-+%5Ctan+%5Cleft%28+%5Cdfrac%7Bx+%2B+y%7D%7B2%7D+%5Cright%29+%5Cright%5D+%3D+x+%2B+c&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002)
(D) None of these
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
17. If  , then
, then  is equal to:
is equal to:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
18. If the shortest distance between the line  and
and  is
is  , then the integral value of ‘
, then the integral value of ‘ ‘ is equal to:
‘ is equal to:
(A) 1
(B) -1
(C) 2
(D) 4
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
19. Given  &
&  are two vertices of the
are two vertices of the  . If the locus of centroid of
. If the locus of centroid of  is
is  then the minimum distance between the locus of the vertex
then the minimum distance between the locus of the vertex 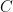 from the line
from the line  is:
is:
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
20. The co-ordinates of a point on the parabola  whose focal distance is 4 is:
whose focal distance is 4 is:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
SECTION B: Numerical Value Type Questions
21. If  and
and  and
and  and
and 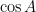 are roots of equation
are roots of equation  . Then the value of
. Then the value of  is:
is:
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Integer Value]
22. For real numbers 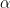 and
and 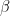 , consider the following system of linear equations:
, consider the following system of linear equations:  ,
,  ,
,  . If the system has infinite solutions, then
. If the system has infinite solutions, then 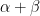 is equal to:
is equal to:
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Integer Value]
23. Number of integral values of parameter  for which
for which  has exactly one local maxima & one local minima is:
has exactly one local maxima & one local minima is:
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Integer Value]
24. Let  and
and  . Then
. Then  is:
is:
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Integer Value]
25. If the foci of the ellipse  and the hyperbola
and the hyperbola  coincide, then the value of
coincide, then the value of  is:
is:
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Integer Value]
