Mathematics Questions
1. The solution of the differential equation  , where
, where  , is:
, is:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
2. Let 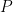 and
and 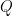 be two square and invertible matrices such that
be two square and invertible matrices such that  , then
, then  is equal to:
is equal to:
(A) Null matrix
(B) 
(C) 
(D) Identity matrix
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
3. A point moves such that the sum of the squares of its distances from four sides of a square of unit length is equal to 3. If the point moves on a circle, then its radius is:
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 9
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
4. The area bounded by the parabola  and the line
and the line  is:
is:
(A) 36
(B) 72
(C) 18
(D) 9
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
5. Common area bounded by regions  and
and  is:
is:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
6. Solution of the differential equation  is given by (where
is given by (where 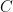 is an arbitrary constant):
is an arbitrary constant):
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
7. If the curve  satisfying
satisfying  passes through
passes through  , then the value of
, then the value of  is:
is:
(A) 8
(B) 16
(C) 24
(D) 12
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
8.  are two foci of the ellipse
are two foci of the ellipse  . Let
. Let 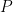 be a point on the ellipse such that
be a point on the ellipse such that  , then the area of
, then the area of  is:
is:
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 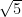
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
9. If a hyperbola centered at the origin has one of its directrices as 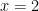 and the ordinate of one of the endpoints of a latus rectum is 12, then find its eccentricity:
and the ordinate of one of the endpoints of a latus rectum is 12, then find its eccentricity:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 2
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
10. Let  . If
. If 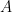 is a skew-symmetric matrix, then
is a skew-symmetric matrix, then  is:
is:
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 0
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
11.  matrices are formed using the elements from the set
matrices are formed using the elements from the set  . Then the number of matrices each of whose trace is at least 7 is:
. Then the number of matrices each of whose trace is at least 7 is:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
12. The image of the circle  with respect to the line
with respect to the line  is:
is:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
13. If 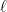 is the length of the latus rectum of the parabola
is the length of the latus rectum of the parabola  , then
, then 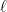 equals:
equals:
(A) 5
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
14. The focus and directrix of a parabola are 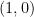 and
and  , respectively. If the length of the latus rectum of the parabola is
, respectively. If the length of the latus rectum of the parabola is  , then the value of
, then the value of  is equal to:
is equal to:
(A) 4
(B) 2
(C) 7
(D) 8
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
15. Eccentricity of the hyperbola conjugate to the hyperbola  is:
is:
(A) 
(B) 2
(C) 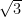
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
16. The eccentric angle of a point on the ellipse  at a distance
at a distance  units from the center of the ellipse is ‘
units from the center of the ellipse is ‘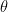 ‘, then the value of
‘, then the value of  is:
is:
(A) 1
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
17. Circle 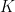 is inscribed in the first quadrant touching the circle
is inscribed in the first quadrant touching the circle  internally. The length of the radius of the circle
internally. The length of the radius of the circle 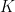 is:
is:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 3
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
18. Solution of the differential equation  is (where
is (where 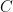 is the constant of integration):
is the constant of integration):
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
19. The focal chord of  is a tangent to
is a tangent to  , then the possible values of the slope of this chord are:
, then the possible values of the slope of this chord are:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
20. Tangents are drawn from every point on the line  to the ellipse
to the ellipse  , then the corresponding chord of contact always passes through the point
, then the corresponding chord of contact always passes through the point  , then
, then  equals:
equals:
(A) 5
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 8
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Option]
21. If  , then the absolute value of the sum of elements of
, then the absolute value of the sum of elements of  is (where
is (where  denotes the adjoint of matrix
denotes the adjoint of matrix 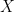 ):
):
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
22. Sum of all possible slopes of tangents to the circle  that pass through the origin is:
that pass through the origin is:
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
23. Area bounded by the curve  and
and  is equal to:
is equal to:
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
24. Let 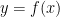 be a real-valued differentiable function on
be a real-valued differentiable function on 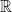 (the set of all real numbers) such that
(the set of all real numbers) such that  . If
. If  satisfies
satisfies  , then the area bounded by
, then the area bounded by  with the
with the  -axis between ordinates
-axis between ordinates 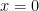 and
and  is equal to:
is equal to:
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
25. Length of the normal chord of the parabola  , which makes an angle of
, which makes an angle of  with the axis of
with the axis of  , is
, is  , then
, then 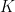 is equal to:
is equal to:
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
