SECTION A: Multiple Choice Questions
1. If  then,
then,  .
.
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 1
(D) -1
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
2. The area bounded by the curve  between
between  and
and  is .
is .
(A) 2
(B) 1
(C) 3
(D) 4
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
3. Area of the region bounded by the curve  and the line
and the line  is
is
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 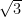
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
4. Area of the region bounded by the curve  ,
,  -axis and the ordinates
-axis and the ordinates 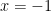 and
and 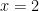 is
is
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
5. The degree of the differential equation  is
is
(A) 2
(B) 1
(C) 3
(D) 4
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
6. The general solution of the differential equation  is .
is .
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
7. The Integrating Factor of the differential equation  is
is
(A) 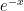
(B) 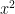
(C) 
(D) 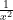
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
8. 
(A) 1
(B) 0
(C) -1
(D) -3
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
9. A unit vector perpendicular to each of the vectors  and
and  is , where
is , where  and
and 
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
10. Area of a rectangle having vertices  and
and 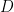 with position vectors
with position vectors  ,
,  and
and  , respectively is .
, respectively is .
(A) 1
(B) 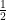
(C) 2
(D) 4
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
11. The Cartesian equation of the line through the point  and which is parallel to the vector
and which is parallel to the vector  is
is
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
12. The shortest distance between the lines  and
and  is .
is .
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
13. The angle between the pair of lines  and
and  is
is
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
14. The coordinates of the corner points of the bounded feasible region are  . The maximum of the objective function
. The maximum of the objective function  is .
is .
(A) 3400
(B) 3000
(C) 2400
(D) 2000
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
15. The maximum value of  subject to constraints
subject to constraints  ,
,  is :
is :
(A) 25
(B) 9
(C) 0
(D) 10
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
16. Two events 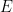 and
and 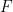 are independent. If
are independent. If  and
and  then
then 
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 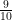
(D) 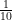
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
17. Let A and B be two events such that  and
and  . Then
. Then  .
.
(A) 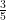
(B) 
(C) 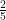
(D) 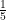
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
18. A man is known to speak truth 4 out of 5 times. He throws a die and reports that it is a six. The probability that actually there was a six is
(A) 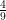
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
19. Let  . Then number of relations containing
. Then number of relations containing  which are symmetric and transitive but not reflexive is .
which are symmetric and transitive but not reflexive is .
(A) 2
(B) 1
(C) 3
(D) 4
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
20. Let  be defined as
be defined as  . Then
. Then 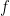 is .
is .
(A) Many – one and onto
(B) One – one and onto
(C) One – one but not onto
(D) Neither one – one nor onto
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
21. ![\tan ^{-1}\left[\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}} \cos \left(5 \sin ^{-1} \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\right]=](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Ctan+%5E%7B-1%7D%5Cleft%5B%5Cfrac%7B%5Csqrt%7B2%7D%7D%7B%5Csqrt%7B3%7D%7D+%5Ccos+%5Cleft%285+%5Csin+%5E%7B-1%7D+%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7B%5Csqrt%7B2%7D%7D%5Cright%29%5Cright%5D%3D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002)
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
22. If  for all
for all ![x \in[-1 / 2,1 / 2]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=x+%5Cin%5B-1+%2F+2%2C1+%2F+2%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) , then
, then
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
23. The number of real solutions of the equation  is
is
(A) 0
(B) 4
(C) 2
(D) 1
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
24.  .
.
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
25. Let 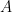 be an invertible square matrix of order
be an invertible square matrix of order  . Then
. Then  is .
is .
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
26. Find the area of a triangle given that midpoints of its sides are  and
and  .
.
(A) 47
(B) 
(C) 94
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
27. If the matrix ![\left[\begin{array}{ccc}x & x^{2}+3 x & 5 \\ -2 x-6 & x^{2} & -4 x-2 \\ 5 & x^{2}+2 & x^{3}\end{array}\right]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Cleft%5B%5Cbegin%7Barray%7D%7Bccc%7Dx+%26+x%5E%7B2%7D%2B3+x+%26+5+%5C%5C+-2+x-6+%26+x%5E%7B2%7D+%26+-4+x-2+%5C%5C+5+%26+x%5E%7B2%7D%2B2+%26+x%5E%7B3%7D%5Cend%7Barray%7D%5Cright%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) is a symmetric matrix, then the value of
is a symmetric matrix, then the value of  is .
is .
(A) 3,2
(B) -3,-2
(C) -3
(D) -2
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
28. If ![\mathrm{A}=\left[\begin{array}{ll}0 & 1 \\ 1 & 0\end{array}\right]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Cmathrm%7BA%7D%3D%5Cleft%5B%5Cbegin%7Barray%7D%7Bll%7D0+%26+1+%5C%5C+1+%26+0%5Cend%7Barray%7D%5Cright%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) , then
, then  .
.
(A) 8 I
(B) 6 I
(C) 6 A
(D) 8 A
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
29. For matrix ![A=\left[\begin{array}{ll}2 & 3 \\ 4 & 5\end{array}\right]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=A%3D%5Cleft%5B%5Cbegin%7Barray%7D%7Bll%7D2+%26+3+%5C%5C+4+%26+5%5Cend%7Barray%7D%5Cright%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) , if
, if  then
then  .
.
(A) 5
(B) 7
(C) -7
(D) -5
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
30. 
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
31. If  , then
, then  $(a \neq 0 ; \theta \neq k \pi, k \in z)$
$(a \neq 0 ; \theta \neq k \pi, k \in z)$
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
32. ![\frac{d}{d x}\left[3 \sin \left(60^{\circ}-x^{\circ}\right)-4 \cos ^{3}\left(30^{\circ}+x^{\circ}\right)\right]=](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Cfrac%7Bd%7D%7Bd+x%7D%5Cleft%5B3+%5Csin+%5Cleft%2860%5E%7B%5Ccirc%7D-x%5E%7B%5Ccirc%7D%5Cright%29-4+%5Ccos+%5E%7B3%7D%5Cleft%2830%5E%7B%5Ccirc%7D%2Bx%5E%7B%5Ccirc%7D%5Cright%29%5Cright%5D%3D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) .
.
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
33. If  is continuous at
is continuous at 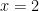 then
then 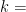
(A) 7
(B) 5
(C) -5
(D) -7
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
34. The total cost  in Rupees, associated with the production of
in Rupees, associated with the production of  units of an item is given by
units of an item is given by  . The marginal cost, where
. The marginal cost, where 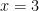 is (in Ruppes)
is (in Ruppes)
(A) 30.15
(B) 30.015
(C) 3.015
(D) 3.15
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
35. The function  is strictly decreasing on .
is strictly decreasing on .
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
36. The absolute minimum value of the function ![f(x)=x^{3}-18 x^{2}+96 x, x \in[0,9]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=f%28x%29%3Dx%5E%7B3%7D-18+x%5E%7B2%7D%2B96+x%2C+x+%5Cin%5B0%2C9%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) is .
is .
(A) 0
(B) 126
(C) -135
(D) -160
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
37. If  , then
, then
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
38. 
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
39. 
(A) 1
(B) 0
(C) 
(D) 2
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
40. 
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
41. The order and the degree of the differential equation ![\sqrt{\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2}}=\sqrt[3]{\left(\frac{d y}{d x}\right)^4+2}](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Csqrt%7B%5Cfrac%7Bd%5E2+y%7D%7Bd+x%5E2%7D%7D%3D%5Csqrt%5B3%5D%7B%5Cleft%28%5Cfrac%7Bd+y%7D%7Bd+x%7D%5Cright%29%5E4%2B2%7D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) is respectively … and …
is respectively … and …
(A) 1,8
(B) 3,2
(C) 2,8
(D) 2,3
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
