Trigonometric Equations
1. The number of solutions of the equation  in
in ![[- \pi, \pi]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5B-+%5Cpi%2C+%5Cpi%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) is:
is:
(A) 5
(B) 7
(C) 6
(D) 9
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
2. The number of solutions of the equation ![(4 - \sqrt{3}) \sin x - 2\sqrt{3} \cos^2 x = -\frac{4}{1 + \sqrt{3}}, x \in [-2\pi, \frac{5\pi}{2}]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%284+-+%5Csqrt%7B3%7D%29+%5Csin+x+-+2%5Csqrt%7B3%7D+%5Ccos%5E2+x+%3D+-%5Cfrac%7B4%7D%7B1+%2B+%5Csqrt%7B3%7D%7D%2C+x+%5Cin+%5B-2%5Cpi%2C+%5Cfrac%7B5%5Cpi%7D%7B2%7D%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) is:
is:
(A) 4
(B) 3
(C) 6
(D) 5
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
3. The number of solutions of the equation ![2x + 3 \tan x = \pi, x \in [-2\pi, 2\pi] - \{\pm \frac{\pi}{2}, \pm \frac{3\pi}{2}\}](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=2x+%2B+3+%5Ctan+x+%3D+%5Cpi%2C+x+%5Cin+%5B-2%5Cpi%2C+2%5Cpi%5D+-+%5C%7B%5Cpm+%5Cfrac%7B%5Cpi%7D%7B2%7D%2C+%5Cpm+%5Cfrac%7B3%5Cpi%7D%7B2%7D%5C%7D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) is:
is:
(A) 4
(B) 5
(C) 3
(D) 6
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
4. If ![\theta \in [-\frac{7\pi}{6}, \frac{4\pi}{3}]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Ctheta+%5Cin+%5B-%5Cfrac%7B7%5Cpi%7D%7B6%7D%2C+%5Cfrac%7B4%5Cpi%7D%7B3%7D%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) , then the number of solutions of
, then the number of solutions of  is equal to:
is equal to:
(A) 7
(B) 10
(C) 6
(D) 8
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
5. If ![\theta \in [-2\pi, 2\pi]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Ctheta+%5Cin+%5B-2%5Cpi%2C+2%5Cpi%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) , then the number of solutions of
, then the number of solutions of  is equal to:
is equal to:
(A) 8
(B) 6
(C) 10
(D) 12
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
6. The sum of all values of ![\theta \in [0, 2\pi]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Ctheta+%5Cin+%5B0%2C+2%5Cpi%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) satisfying
satisfying  and
and  is:
is:
(A) 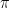
(B) 
(C) 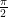
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
7. Let ![|\cos \theta \cos(60 - \theta) \cos(60 + \theta)| \leq \frac{1}{8}, \theta \in [0, 2\pi]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%7C%5Ccos+%5Ctheta+%5Ccos%2860+-+%5Ctheta%29+%5Ccos%2860+%2B+%5Ctheta%29%7C+%5Cleq+%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7B8%7D%2C+%5Ctheta+%5Cin+%5B0%2C+2%5Cpi%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) . Then, the sum of all
. Then, the sum of all ![\theta \in [0, 2\pi]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Ctheta+%5Cin+%5B0%2C+2%5Cpi%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) where
where  attains its maximum value, is:
attains its maximum value, is:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
8. The number of solutions of the equation ![4 \sin^2 x - 4 \cos^3 x + 9 - 4 \cos x = 0; x \in [-2\pi, 2\pi]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=4+%5Csin%5E2+x+-+4+%5Ccos%5E3+x+%2B+9+-+4+%5Ccos+x+%3D+0%3B+x+%5Cin+%5B-2%5Cpi%2C+2%5Cpi%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) is:
is:
(A) 0
(B) 3
(C) 1
(D) 2
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
9. If  has exactly 3 solutions in the interval
has exactly 3 solutions in the interval ![[0, \frac{n\pi}{2}]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5B0%2C+%5Cfrac%7Bn%5Cpi%7D%7B2%7D%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) ,
, 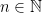 , then the roots of the equation
, then the roots of the equation  belong to:
belong to:
(A) 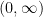
(B) 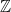
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
10. The sum of the solutions  of the equation
of the equation  is:
is:
(A) 3
(B) 1
(C) 0
(D) -1
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
11. If  is the solution of
is the solution of  , then the value of
, then the value of  is:
is:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
12. If  has exactly 7 solutions in the interval
has exactly 7 solutions in the interval ![[0, \frac{n\pi}{2}]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5B0%2C+%5Cfrac%7Bn%5Cpi%7D%7B2%7D%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) , for the least value of
, for the least value of 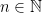 , then
, then  is equal to:
is equal to:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
13. The number of elements in the set  is:
is:
(A) 9
(B) 8
(C) 12
(D) 10
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
14. Let  and
and  , then
, then  is equal to:
is equal to:
(A) 16
(B) 32
(C) 8
(D) 64
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
15. The number of elements in the set  is:
is:
(A) 1
(B) 3
(C) 0
(D) infinite
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
16. Let  . Then:
. Then:
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
17. Let  . Then
. Then  is equal to:
is equal to:
(A) 0
(B) -2
(C) -4
(D) 12
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
18. The number of solutions of  , such that
, such that  is:
is:
(A) 4
(B) 6
(C) 8
(D) 12
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
19. Let for some real numbers 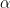 and
and 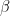 ,
,  . If the system of equations
. If the system of equations  and
and  has more than one solution, then
has more than one solution, then  is equal to:
is equal to:
(A) 
(B) 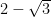
(C) 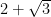
(D) 
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
20. The number of solutions of the equation  ,
, ![x \in [-3\pi, 3\pi]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=x+%5Cin+%5B-3%5Cpi%2C+3%5Cpi%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0&c=20201002) is:
is:
(A) 8
(B) 5
(C) 6
(D) 7
Click to View Answer
Correct Answer: [Insert Correct Answer]
